As consumer demand for tooth-whitening intensifies, color relapse has become a core pain point—yet its consequences go beyond aesthetics. Repeated or frequent whitening treatments not only prompt users to undergo multiple bleaching cycles but can also disrupt the oral ecosystem, causing unintended oral microbiome impact. Thus, B2B manufacturers must balance long-lasting shade durability with microbiome health when formulating and designing products.
First, it’s essential to understand why teeth revert after whitening:
Typically, relapse becomes noticeable 2–4 weeks post-treatment, with pigment retention correlating to biofilm formation.
Next, bleaching agents exert conflicting pressures on oral bacteria:
Therefore, in pursuing whitening effectiveness, manufacturers must evaluate oral microbiome impact to prevent dysbiosis.Company web: https://www.powsmart.com/product/electric-toothbrush/
Moreover, plaque biofilm formation is tightly linked to color relapse:
Controlling biofilm growth is therefore key to delaying shade relapse and preserving a healthy microbiome.
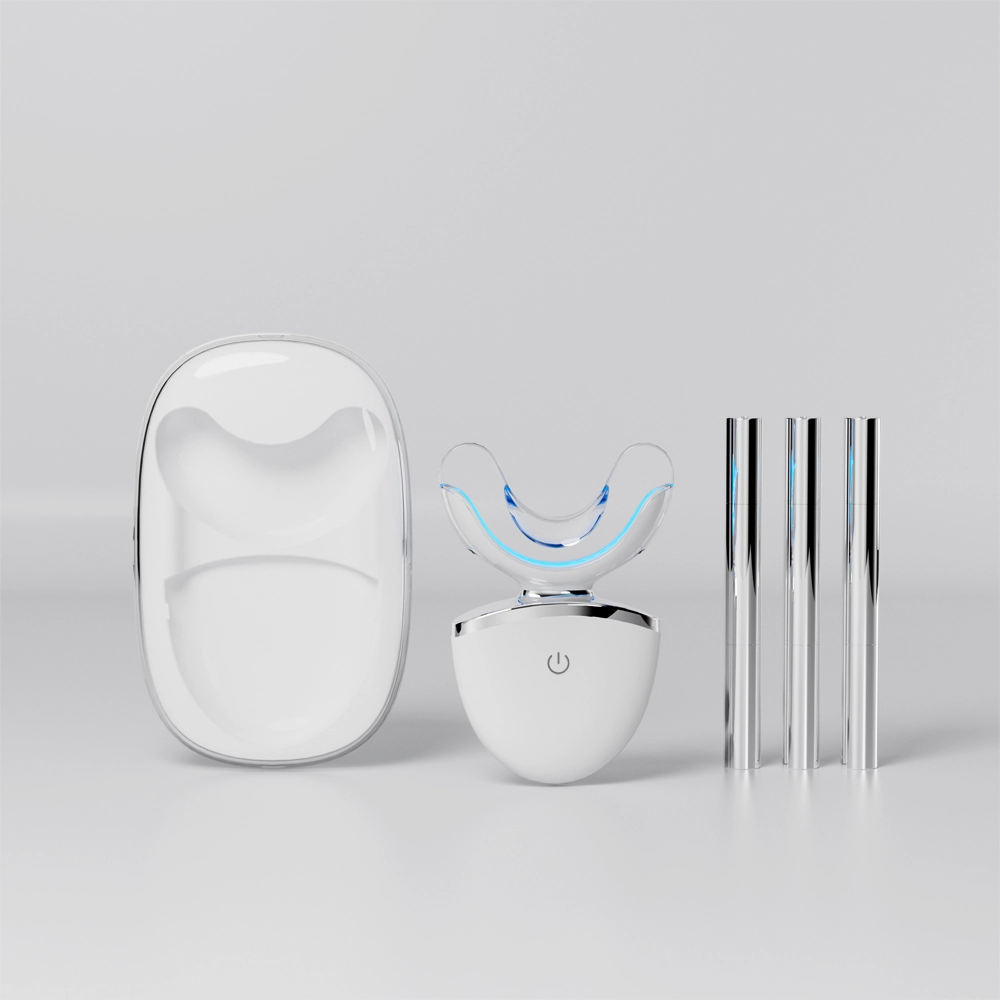

To address these challenges, B2B formulators can optimize their products by:
This “whitening + microbiome” approach helps mitigate color relapse while limiting oral microbiome impact.
In addition, hardware and protocols play a pivotal role:
Coordinating chemistry, mechanics, and software enables effective, long-lasting whitening without harming the oral ecosystem.
Finally, sustaining results requires comprehensive aftercare:
A full-cycle education and management strategy helps B2B partners maximize customer satisfaction and retention.
Conclusion
Color relapse is more than a cosmetic setback—it directly influences oral microbiome impact. Only by integrating balanced formulations, advanced device protocols, and robust aftercare can manufacturers achieve both enduring whitening and a stable oral ecosystem. To explore “whitening + microbiome” innovations, please contact our development team!


Why Combine Quality Certification Support with a Global Logistics Partner for International Markets?
.jpg)
Gingival Burns Alongside Cervical Hypersensitivity – Urgent?
.jpg)
Does LED Light Malfunction Worsen Enamel Abrasion Concerns?
.jpg)
Why Optimize Light Diffusion Lens Design Based on Peroxide Decomposition Rate?
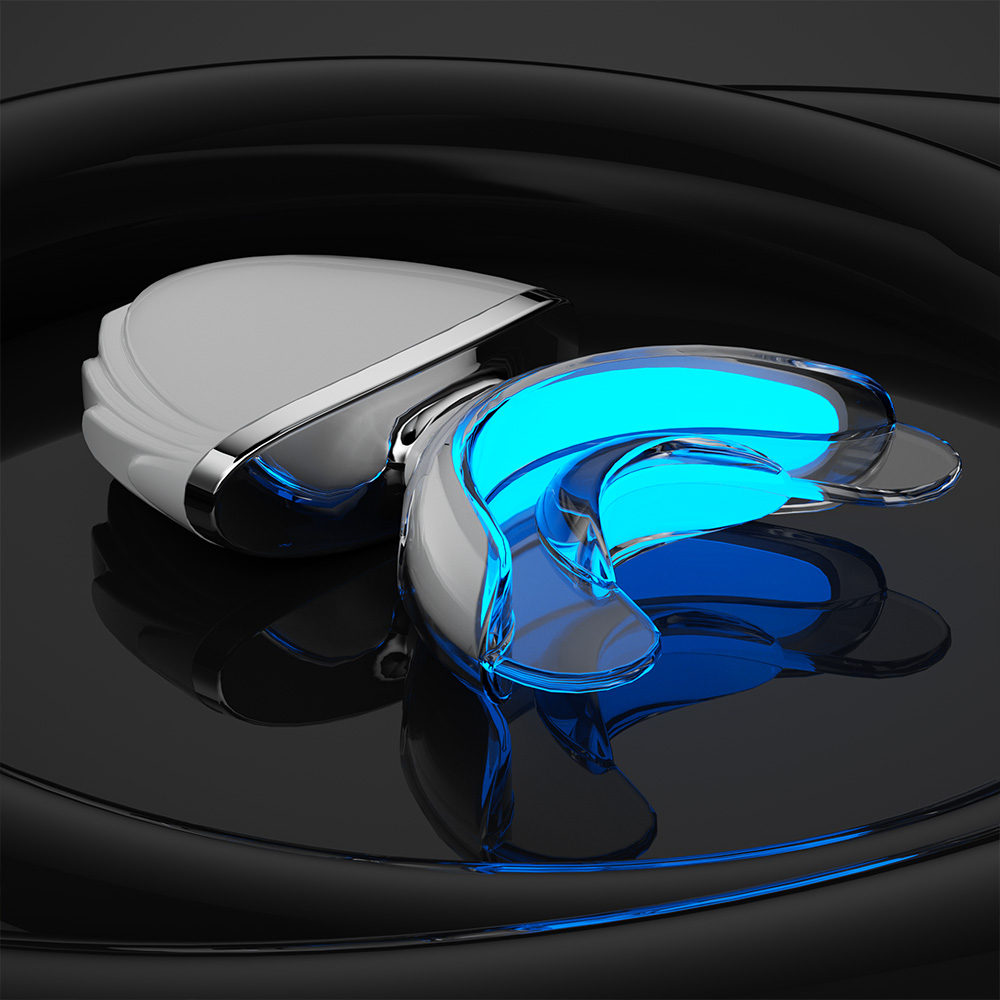

The process of brand owners customizing OEM whitening teeth Kit
.jpg)
Child Compatibility Meets Cold Light Sensitivity: Safe?
Oral Care Products CPSR Material List: Ensuring Safety and Compliance
.jpg)
How Does Allergen Testing Prevent Bleach Residuals?
.jpg)
Allergic Reactions After Pulp Irritation – Coincidence?

What Are the Other Promising oral care Products in the Oral Care Industry?

How Does a Contract Manufacturing Agreement Secure a Steady Brush Head Replacement Supply?

Capitalizing on the LED Oral Care Boom: Essential Market Insights for Brands
.jpg)
How Does Cold Light Wavelength Affect Bleach Decomposition?

How Can oral care Brand Owners Enhance brand influenceThrough Product Expansion Strategies?
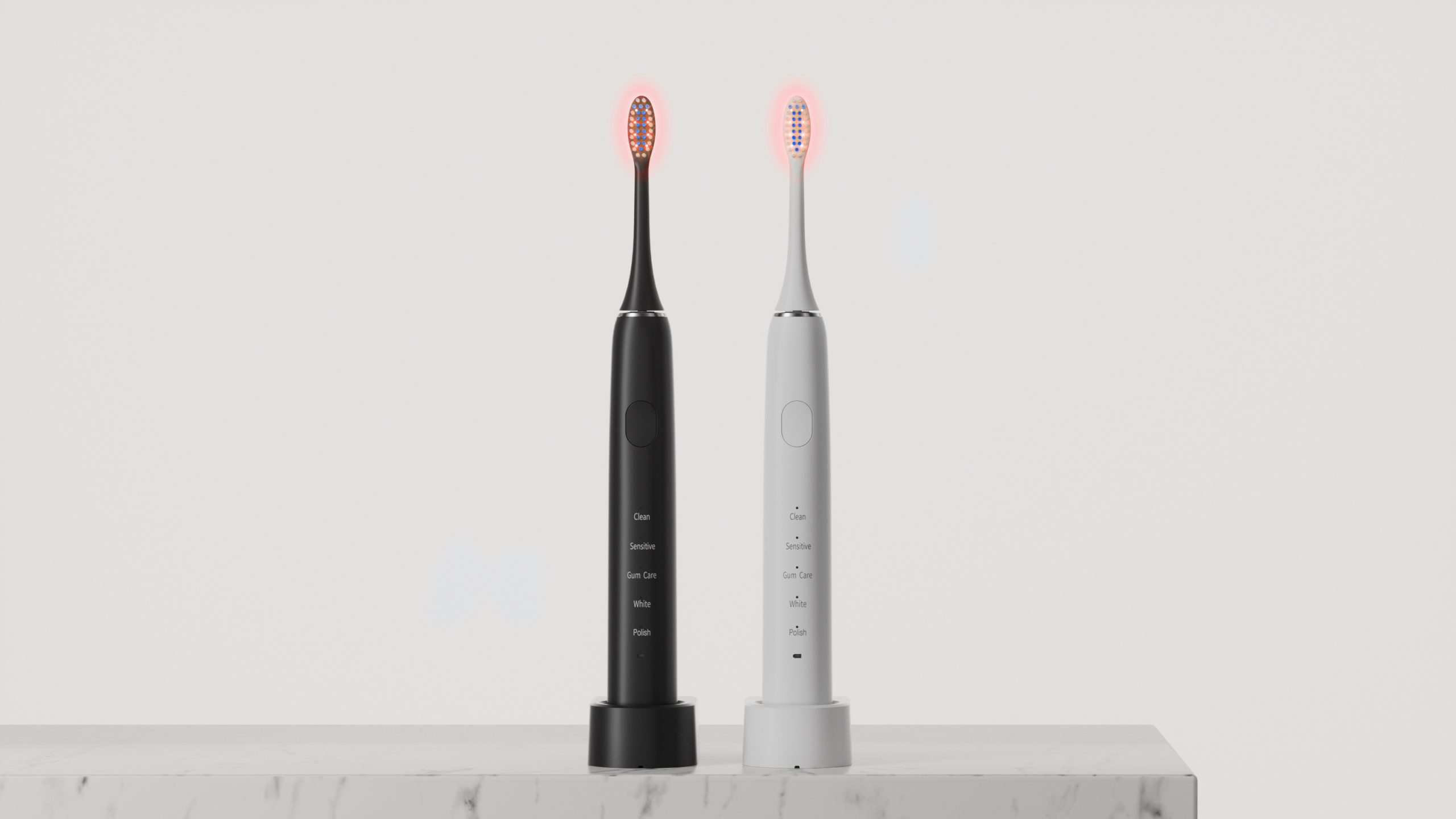

The Science of Light: How Red & Blue LED Technology Enhances Modern Oral Care

What Are the Advantages of Home Dental Beauty Products?