In the realm of personal care device design, especially in products like sonic toothbrushes and water flossers, vestibular stimulation and head positioning are rarely discussed together. Yet, users occasionally report dizziness, vertigo, or disorientation after prolonged device use. Could vestibular stimulation caused by device vibrations or water jets, coupled with specific head positioning, be a hidden cause of user discomfort? This blog delves deep into this overlooked topic to clarify its impact on user experience and product safety.
Vestibular stimulation refers to any mechanical input—vibrations, water pulses, or sonic waves—that interacts with the inner ear’s balance system. In oral care devices:
These stimuli, though intended for cleaning efficiency, may inadvertently affect the vestibular apparatus, especially in sensitive users.
Head positioning plays a crucial role in vestibular response:
Understanding head angles during use is thus essential in ergonomic and mechanical design. Company web:https://www.powsmart.com/product/electric-toothbrush/
The short answer: yes. Combined exposure to:
These factors can stimulate the semicircular canals, leading to transient disorientation or dizziness. While not harmful for most users, it poses comfort risks for:
.jpg)
To minimize vestibular-induced head positioning discomfort:
Adapting product engineering and user education can greatly enhance perceived safety.
Before mass production:
Comprehensive pre-market evaluations ensure real-world reliability and reduce post-sale complaints.
Rather than ignoring vestibular stimulation risks, manufacturers can transform them into a quality guarantee:
By addressing dizziness risks proactively, B端厂家 strengthen partnerships with retailers and distributors prioritizing consumer well-being.
Could vestibular stimulation combined with improper head positioning be causing your customers’ dizziness complaints? Quite possibly. Recognizing this subtle interaction is the first step toward building safer, more comfortable oral care products. Manufacturers prioritizing human-factor engineering in tandem with mechanical optimization will lead the market in both safety and satisfaction. Contact us
.jpg)
Supermarket Toothbrush Bulk Supply for Global Retail Chains

Bulk Personalized Electric Toothbrush: Custom Manufacturing Services
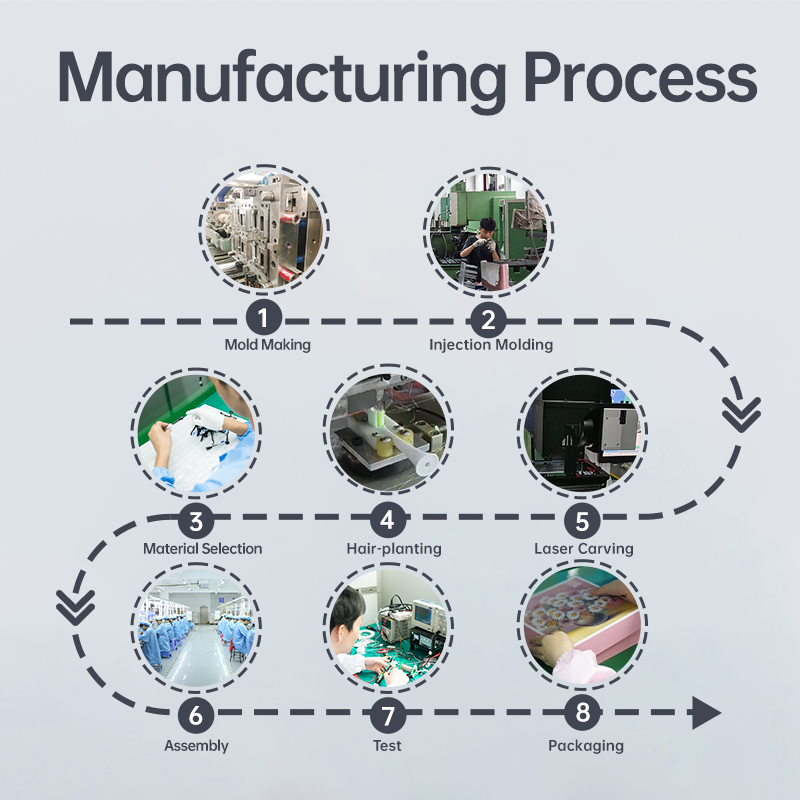
A Guide to the Entire Process of OEM Teeth Whitening Device: Detailed Explanation of Every Step from Design to Mass Production

How Do Toothbrush Design Services Accelerate Toothbrush Prototype Development?
.jpg)
Professional Whitening Device for Spas
.jpg)
Are You the Leading Water Flosser Nozzle Supplier for High-Volume Replacement Head Production?

Low Pressure Water Flosser for Tonsil Stones: Specialized Solutions From The Manufacturer

Is It Bad to Use a Dental Water Flosser Every Day?
.jpg)
Can Contact Oxidation Lead to Weak Pressure?
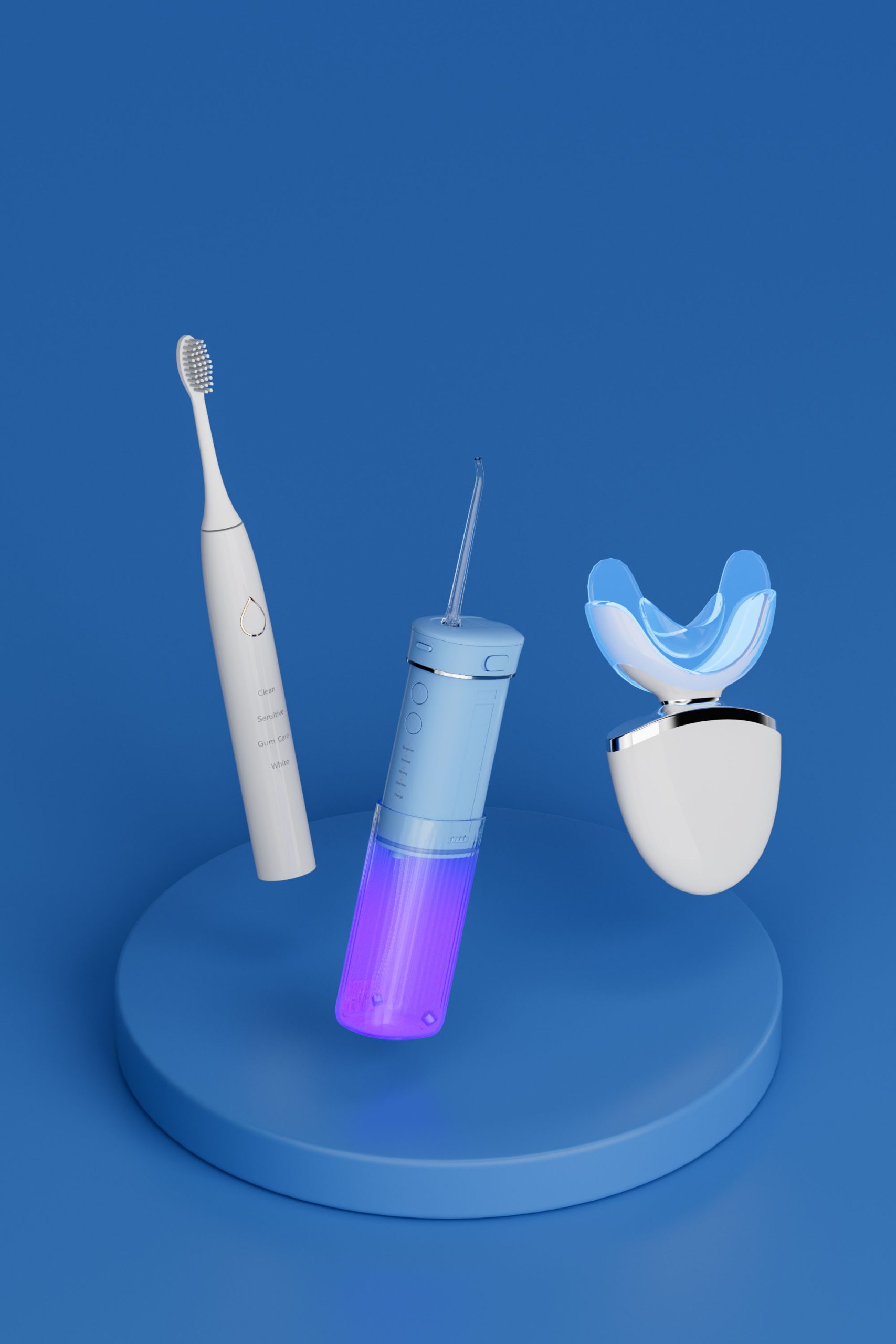
A Successful Case of OEM ODM Teeth Whitening Devices: How Did a Cross-Border Brand Rise Rapidly Through OEM?

Common Water Flosser Problems and How to Fix Them
.jpg)
Kids Electric Toothbrush Bulk Supplier | School and Clinic Programs

Targeting Specific Product Features for Successful OEM Partnerships
.jpg)
Innovative Teeth Whitener Solutions | Specialized Production Line
.jpg)
Poor Contact and Batch Defects Eroding Trust?

Teeth Whitener Regulations in EU & US: Strategic OEM Manufacturing Insights