Material degradation in oral care devices, such as electric toothbrushes and water flossers, is an often-overlooked issue. Yet, it can quietly lead to the release of harmful chemical residue into the user’s mouth, raising significant health concerns. For B2B manufacturers, this is not just a matter of consumer trust but also a critical compliance and product lifecycle issue. This blog will dissect the causes, risks, and prevention strategies related to material breakdown and chemical contamination in oral hygiene devices.
Material degradation refers to the physical or chemical breakdown of components over time due to factors like:
As the material degrades, microscopic particles or chemical residue may leach from brush heads, water tanks, seals, or internal tubing—especially in low-cost devices or poorly stored stock.
When chemical residue enters the mouth, it may:
For children and users with oral ulcers or compromised immunity, the consequences may be more severe, requiring clinical attention. Company web: https://www.powsmart.com/product/electric-toothbrush/
The following design and manufacturing oversights can significantly speed up material degradation:
In addition, devices stored long-term in high-humidity environments, such as warehouse stock without climate control, are highly vulnerable.
Manufacturers and distributors should monitor for these early indicators:
These signs often precede more severe health-related reports, making proactive detection vital.
To reduce the risk of chemical residue caused by material degradation, consider the following:
These enhancements not only protect end users but also reduce warranty claims and ensure smoother regulatory approvals.
Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, CE, and China’s NMPA are paying increasing attention to chemical safety in consumer products. Failing to manage material degradation risks may lead to:
Thus, investing in safe materials isn’t just ethical—it’s a strategic safeguard.
Material degradation and the resulting chemical residue are silent threats that can compromise both product safety and business credibility. For B2B oral care device manufacturers, early attention to material selection, chemical compatibility, and quality control processes is essential. At our manufacturing facility, we integrate advanced testing and certified materials to ensure every product delivered is safe, durable, and regulation-ready. Contact us
.jpg)
Brush + Flosser Combo Electric Toothbrush Wholesale

Don’t Fall for These Viral Teeth Whitening Trends: Dentist-Approved whitening
.jpg)
Is Toothbrush Production Keeping Up with Toothbrush Technology Trends?

Electric Toothbrush Low-Noise × Sonic Vibration: Silent Tech for Smarter Brushing
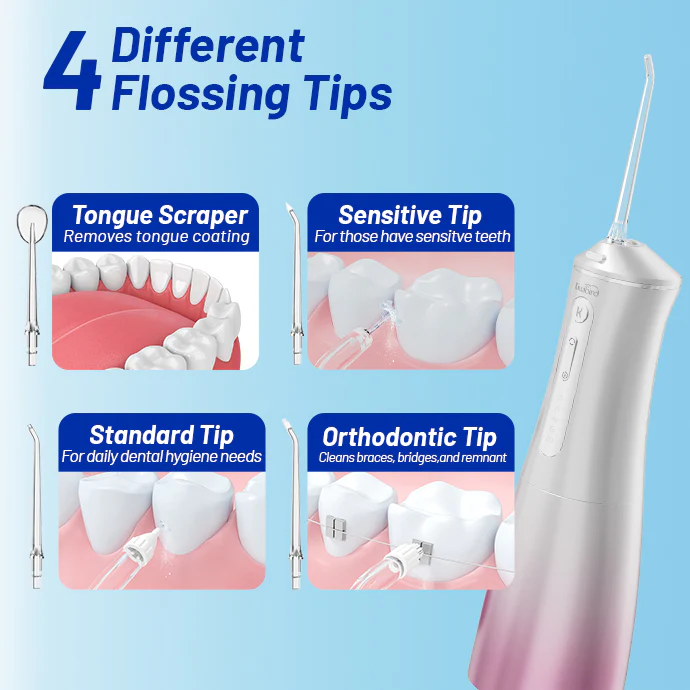
What is Sonic Technology in Sonic Electric Toothbrush?
.jpg)
Bristle Hardening Inducing Gum Recession – Brushing or Destroying?
How Does Integrated Brush Head Sterilization Add Value to Travel Case Manufacturing?

Which Teeth Whitening Products Actually Work? An OEM Manufacturer’s Evidence-Based Guide

Is your sonic toothbrush Dallas equipped for the ultimate Dallas oral health defense?
.jpg)
Electric Toothbrush with Wireless Charging OEM
Deep Clean Interdental Electric Toothbrush Manufacturing Solutions

How Does Minimizing Chromatic Aberration Boost Luminescence Efficiency in LED Whiteners?

Why Partner with a Global Logistics Partner under a Contract Manufacturing Agreement?

How to Choose a Reliable Electric Toothbrush Factory?

Maximizing Profit Margins: How to Position Water Flossers as Premium Products

Which Electric Toothbrush With Whitening Works Best?