In the field of professional oral care devices, user safety incidents such as gingival burns combined with cervical hypersensitivity are emerging as an urgent concern, especially in the whitening and deep-cleaning product categories. Manufacturers may underestimate the combined impact of thermal, chemical, and mechanical stress on delicate gingival and cervical areas. But when burns and hypersensitivity appear together, they signal a systemic design or process flaw that must be addressed. How urgent is this issue—and how can product design prevent it?
Gingival burns refer to tissue damage along the gums, typically caused by:
Cervical hypersensitivity involves intense sensitivity in the tooth neck region (cementoenamel junction), often triggered by:
When these two issues occur simultaneously, user discomfort and potential oral injury escalate rapidly.
Experiencing gingival burns and cervical hypersensitivity together is not random:
Therefore, these two complaints often indicate a shared design flaw—typically excessive thermal output, poor gel formulation, or poorly shaped delivery heads. Company web:https://www.powsmart.com/product/electric-toothbrush/
Common risk factors contributing to combined injuries include:
Manufacturers must recognize that tissue safety depends on more than formulation or output specs—it requires full-system safety integration.
Effective design changes to prevent gingival burns and cervical hypersensitivity include:
Applying these design principles at R&D level can proactively eliminate root causes.
In mass production, manufacturers should implement:
These controls help detect risks that might otherwise bypass traditional mechanical testing.
By eliminating the combined risk of gingival burns and cervical hypersensitivity, manufacturers can:
In professional B2B sales, safety-focused certifications and test reports can differentiate products in competitive tenders or regulatory audits.
Yes, when gingival burns occur alongside cervical hypersensitivity, it signals an urgent systemic problem—one that requires immediate intervention at the design and QA levels. By understanding the link between thermal, chemical, and mechanical stresses, manufacturers can protect users more effectively and transform safety into a powerful market differentiator. Contact us
.jpg)
.jpg)
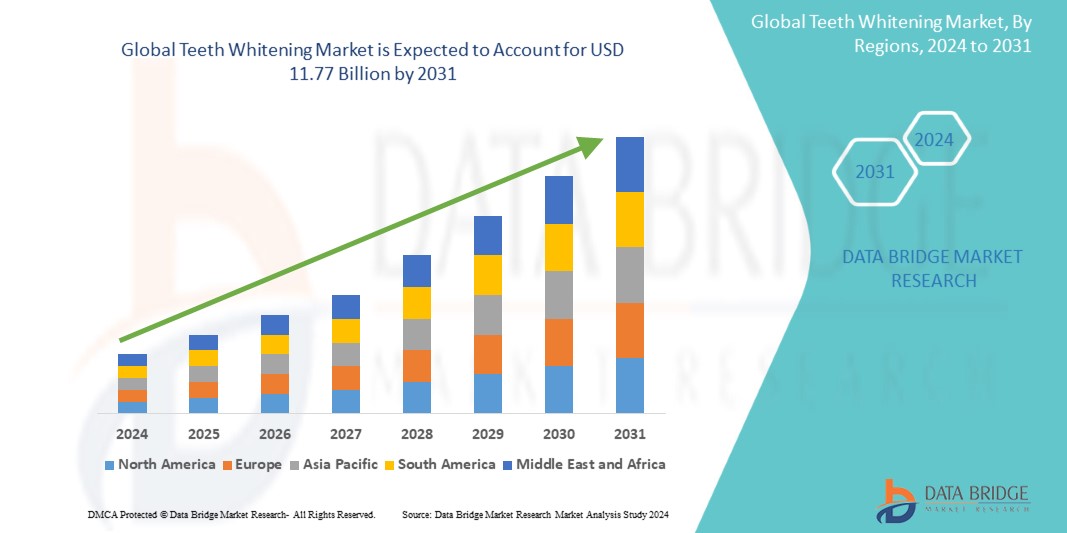
Global teeth whitening Device Market : Fastest Growing Regions and Consumer Group Portraits
.jpg)
Wireless Charging Toothbrush Factory | Contactless Power for Modern Hygiene
.jpg)
Electric Toothbrush Quality Inspection and OEM Testing Standards

Technique Affecting Periodontal Pocket – How Deep Is the Impact?
.jpg)
App-Enabled Toothbrush Bulk Orders | Smart Oral Care Solutions

How to Care for Your Teeth While Traveling? Essential Oral Hygiene Tips for Travelers

How Can a Dental Clinic Partnership Help You Penetrate the Home Appliance Market?

Finding the Right Kids’ Toothbrush: An OEM Guide to U-Shaped vs. Sonic Options
.jpg)
Pulse Instability with Noise Spikes – Motor Dying?
How much does it cost to manufacture a toothbrush?

Brooklyn Fast Local Delivery Electric Toothbrush Wholesale Suppliers
.jpg)
Chip Overheating with Cavity Acceleration – Hidden Link?
.jpg)
Electric Toothbrush Supplier Alabama | Corporate & Dental Partners

Why Adopt Latest Toothbrush Manufacturing Technology to Meet Toothbrush Production Standards?
.jpg)
Jet Stream Water Flosser – High-Pressure Oral Irrigator

Is Your Kids-safe Design Verified to Use Non-toxic Material?