In an era of rapidly evolving device ecosystems, charger mismatch has emerged as a surprisingly common issue with significant consequences. When chargers are poorly specified or incorrectly paired, they often result in battery incompatibility, posing both performance and safety risks. This article explores how mismatched charging components can undermine battery lifespan and reliability—and what manufacturers can do to prevent these costly failures.
Charger mismatch refers to situations where the charger’s output characteristics—such as voltage, current, or connector type—do not align with the device’s battery requirements. This can happen for several reasons:
Even minor deviations in output specifications can gradually degrade battery health or trigger immediate charging failures.
Battery incompatibility can present through a range of observable symptoms:
These symptoms are often mistakenly attributed to defective batteries, when the real culprit is an incompatible charger. Company web:https://www.powsmart.com/product/electric-toothbrush/
From a B2B perspective, charger mismatch is not just a consumer inconvenience—it’s a liability. When customers unknowingly use incompatible chargers:
Manufacturers must therefore design clear safeguards to protect both users and their own operations.
Beyond obvious hardware failures, repeated battery incompatibility accelerates long-term degradation:
Additionally, disposal costs rise, as batteries that fail prematurely often cannot be recycled easily due to safety hazards.
Fortunately, several proven strategies can mitigate these risks:
These steps help ensure every charge cycle remains safe and effective.
While charger mismatch is often overlooked, proactively addressing it can set your brand apart. Devices engineered with intelligent compatibility safeguards build user trust, reduce support costs, and strengthen product differentiation in a crowded market.
Ultimately, charger mismatch and battery incompatibility are not minor technical oversights—they are critical vulnerabilities that can damage user experience and brand equity. By investing in precise engineering and clear user education, manufacturers can deliver devices that perform reliably throughout their intended lifespan.
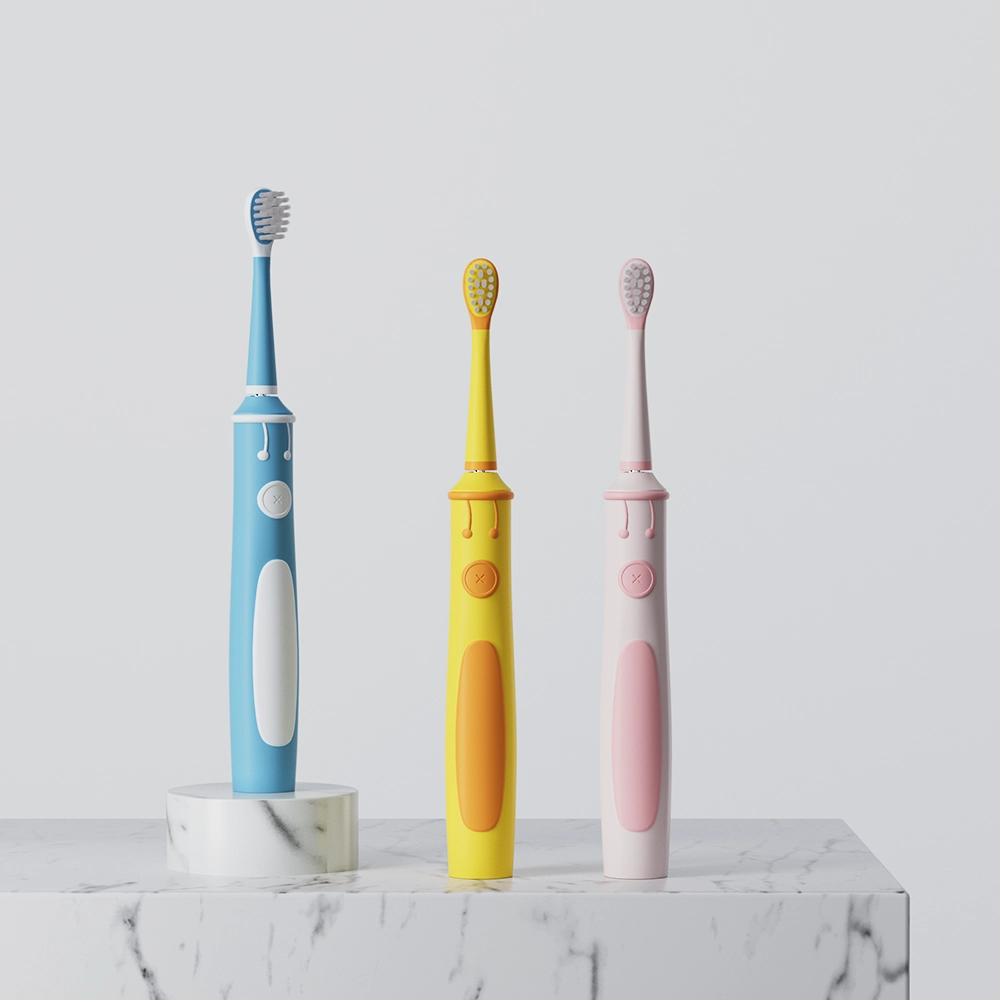
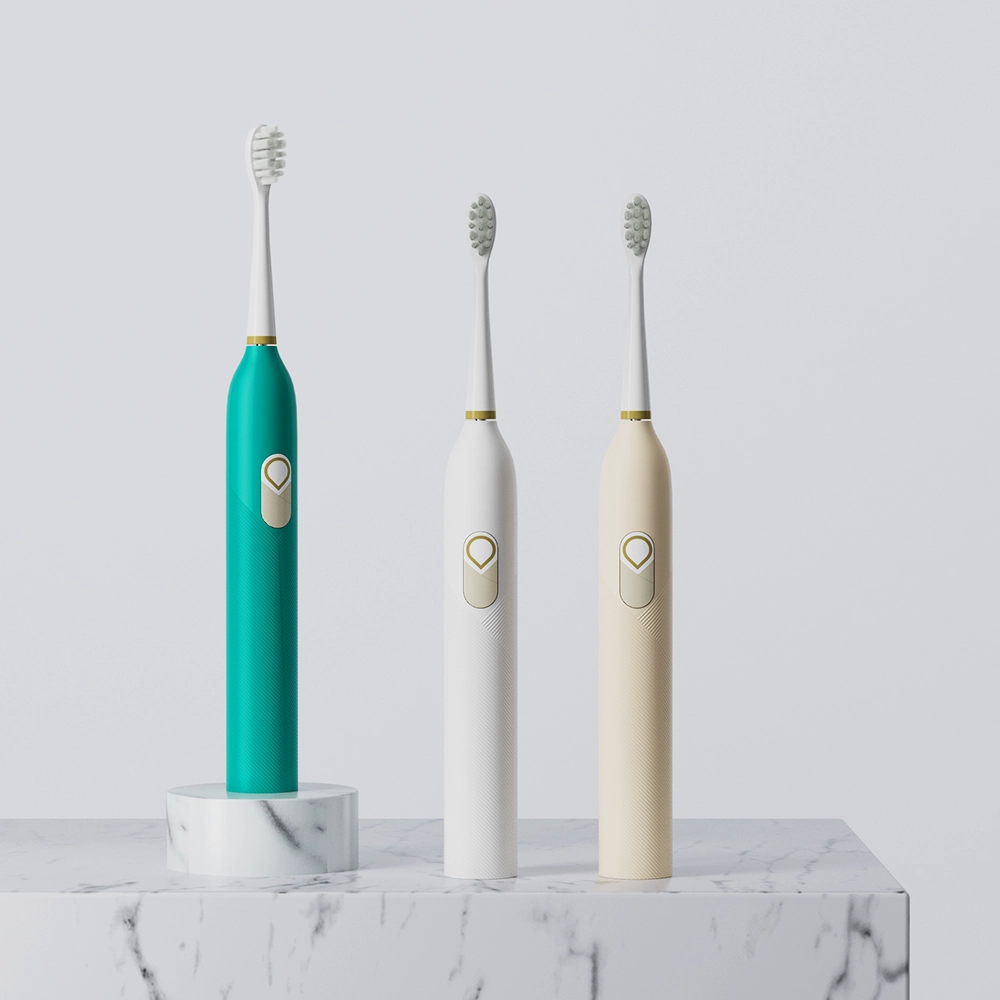


.jpg)
sonic electric toothbrush Sacramento
Head Detachment with Tank Cracks—Replace All?

Innovating a Whitening Gel Formula for Your Cosmetic Product Development
Mouth Ulcers After Allergic Rashes – Coincidence?
Grip Fatigue with Noise Pollution – Design Flaw?
Sonic Toothbrush Export from China | OEM/ODM Professional Supplier
Tooth Chipping Alongside Root Darkening – Irreversible?
.jpg)
Sourcing Sonic Toothbrush B2B for Your Role as a Hotel Amenity Supplier?
Gum Bleaching from Pulpitis Risk – Whitening Gone Wrong?
.jpg)
Why Choose a Water Flosser for Sensitive Gums as a Core Gentle Oral Care Product?
Sync Errors Causing Taste Distortion – Tech Glitch?
Portable LED Teeth Whitening Device Supplier

How Consumption Upgrading Is Redefining Oral Care Product Development
1-scaled.jpg)
The Growing Demand for At-Home Teeth Whitening & What It Means for Brands
electric toothbrush with AI sensor supplier
Looking for an OEM Partnership Program that Guarantees Long-Term Toothbrush Supply?

electric toothbrush heads Deep Clean

Customization Teeth Whitening Gel

electric toothbrush heads Ultra Soft
.jpg)
Florida Electric Toothbrush – Powsmart PTR-C8

electric toothbrush heads Charcoal Infuse-Round

Private Label Whitening Gel

electric toothbrush heads Regular Clean

Electric toothbrush heads Charcoal Infused-Diamond
whstapp
whstapp
National Toll-Free Service Hotline
+86 755 86238638