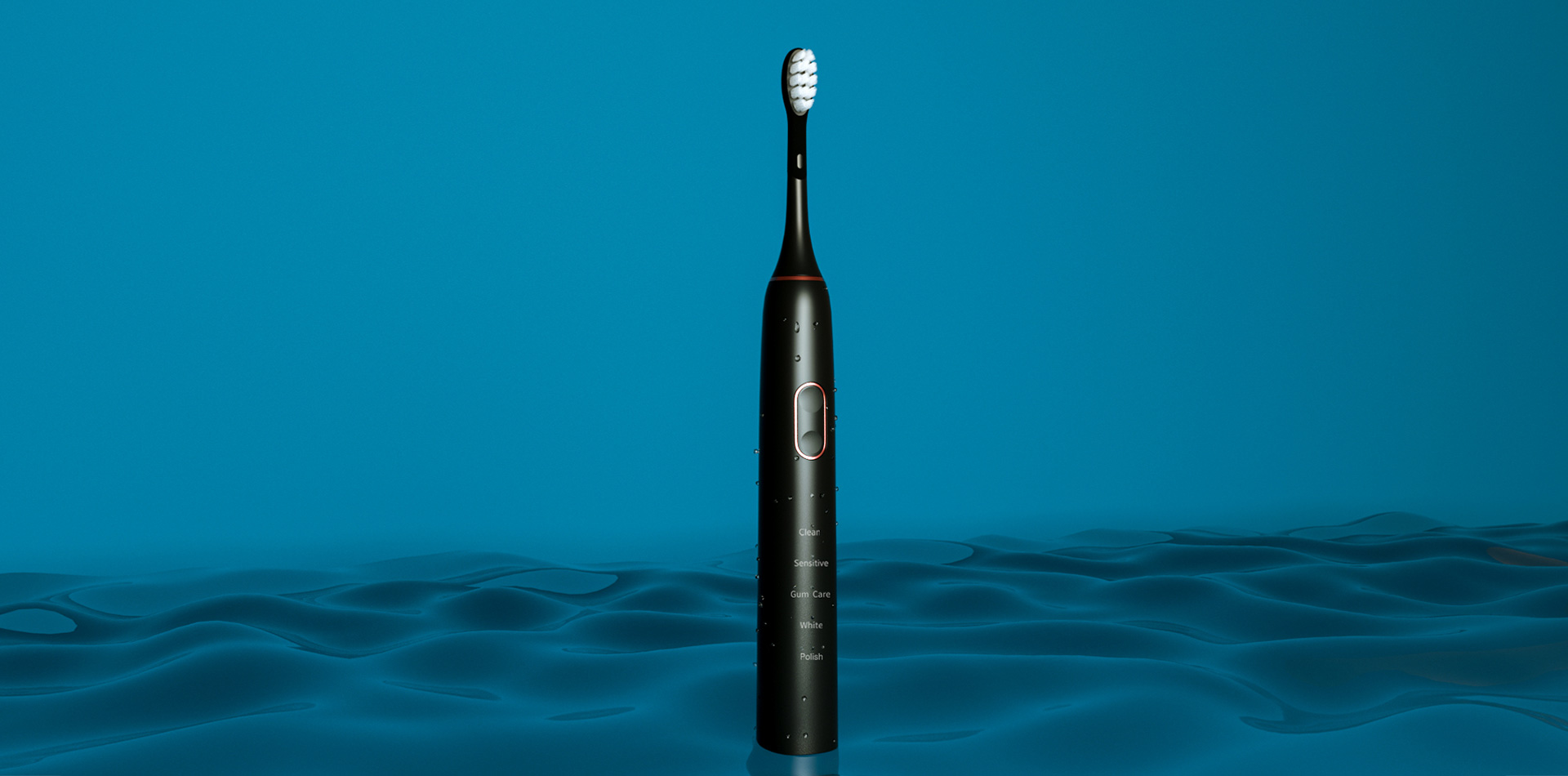
In OEM electric toothbrush production, the Brush Head Attachment Mechanism plays a decisive role in shaping the entire Toothbrush Mold Design. Because the attachment interface defines how the brush head connects, rotates, transmits force, and maintains long-term stability, it becomes one of the core engineering factors manufacturers must consider at the earliest design stage. An optimized mechanism ensures durability, cost-efficiency, and seamless compatibility across multiple product lines.
Snap-fit, twist-lock, magnetic, and spline-driven Brush Head Attachment Mechanisms each require different internal geometries. These variations directly influence Toothbrush Mold Design, dictating cavity layout, internal ribbing, and thickness distribution.
The way brushing torque is transferred—from the motor shaft through the attachment point—affects the reinforcement areas inside the handle mold. A stable Brush Head Attachment Mechanism helps determine rib patterns, core-pin placement, and tolerance strategies during injection molding.
Because the attachment interface must maintain micrometer-level accuracy for performance and safety, the Toothbrush Mold Design must account for shrinkage rates, deformation control, and precision tooling. High-tolerance mechanisms often increase mold cost and require refined steel choices.
The mechanism interface experiences repeated insertion cycles and rotational stress. This means that both the brush head connector and the handle housing require materials suited for fatigue resistance. Mold design engineers must consider reinforced polymers, glass-filled resins, or multi-material molding to support the Brush Head Attachment Mechanism.
Different attachment systems require different automation sequences. Whether inserting metal shafts, aligning splines, or bonding magnetic components, these steps influence how the Toothbrush Mold Design supports downstream manufacturing. Mold engineers must plan for alignment features, sensor points, and assembly access.
Brands often want multiple toothbrush models to share the same brush head. A standardized Brush Head Attachment Mechanism allows the OEM to reuse core mold components. This reduces production cost, simplifies maintenance, and improves overall SKU management.
The Brush Head Attachment Mechanism is far more than a functional connector—it is a structural, mechanical, and manufacturing anchor point that drives the entire Toothbrush Mold Design strategy. OEMs that prioritize this interface early in the design process achieve better production efficiency, more reliable performance, and greater cross-model compatibility. Contact us

.jpg)
Are Water Flosser Packaging Solutions Key to Secure Water Flosser Export Packaging?

How Does a Custom Brush Handle Mold Support a Calcified Deposit Remover Mechanism?

How to Make Your Own Toothbrush Brand with OEM/ODM Solutions
.jpg)
How Does a Water Flosser OEM Enhance the Efficacy of a Dental Water Flosser for Clinical Use?
Can Cavitation Cleaning Technology Achieve Optimal Results with a Micro-perforated Brush Head Design?
.jpg)
sonic electric toothbrush San Francisco
.jpg)
Can Sustainable Water Flosser Material Sourcing Enhance Water Flosser Design Services?

Why Is Bristle Configuration Design Critical for Saline Solution Compatibility in Irrigators?
.jpg)
Dentist Clinic Electric Toothbrush Supplier

How Long Should I Use Blue Light on My Teeth? OEM Manufacturer’s Guide
.jpg)
San Francisco electric toothbrush supplier

Electric Toothbrush Manufacturers Tell You the Truth About Charcoal Toothbrush Heads
.jpg)
Sonic Toothbrush Factory for Brands | OEM & Private Label Production

Electric Toothbrush Battery Life: A Key OEM Consideration for Product Competitiveness

Finding the Right Kids’ Toothbrush: An OEM Guide to U-Shaped vs. Sonic Options

Do U-shaped Toothbrushes Actually Work? An OEM Manufacturer’s Analysis