For electric-toothbrush OEMs and brands, charging is a small interaction that hugely influences user perception. Wireless Charging (inductive) removes fiddly exposed ports and transforms charging into a seamless, elegant ritual. In turn, a well-designed Charging Dock becomes a visible brand touchpoint on the bathroom counter. Below are six manufacturer-focused dimensions — from UX and enclosure reliability to electrical engineering and commercialization — that explain why and how inductive charging upgrades both product experience and product economics.
First and foremost, Wireless Charging simplifies the user story: drop the handle on the Charging Dock, see a status LED, and be confident the device charges. Consequently:
Furthermore, removing exposed ports lets industrial designers pursue sleeker, sealed forms:
Crucially for bathroom appliances, inductive designs improve ingress protection and hygiene:
On the engineering side, inductive charging is a system design challenge:
Moreover, inductive systems affect cost and operations:
Finally, the Charging Dock is a merchandising and service lever:
Conclusion:
When executed as a product-system — mechanical design, electrical architecture, thermal controls, manufacturing and channel strategy — Wireless Charging makes charging feel effortless and elegant. In addition, a thoughtfully designed Charging Dock becomes a visible expression of brand quality and a recurring-revenue vector rather than a simple accessory. If you’d like, I can turn this into a two-page engineering brief (coil spec, driver block diagram, IP strategy and production QC checklist) to help your teams prototype a dock-enabled toothbrush SKU. Contact us
.jpg)
.jpg)

How to choose an electric toothbrush for the First-Time User ?
Magnetic Levitation Toothbrush Factory: Premium OEM Services
.jpg)
College Student Electric Toothbrush Boston
.jpg)
Can a Cold Light Whitening Kit ODM Guarantee Safety with Gum-Safe Whitening Gel?

Why Pair a Magnetic Levitation Motor with an Optimized Wireless Charging Coil in Premium Electric Toothbrushes?
How to Start a Teeth Whitening Business
.jpg)
long battery life electric toothbrush OEM | High-End Rechargeable Toothbrush Manufacturer
.jpg)
Executive Gift Electric Toothbrush Box Set for Diwali

How Does a Teeth Whitening OEM Optimize Formulas for a Fast-Acting Whitening Gel?

Application and Effectiveness of Electric Toothbrush in Oral Care

What’s the Most Effective Way to Whiten Teeth at Home? An OEM Factory’s Insight
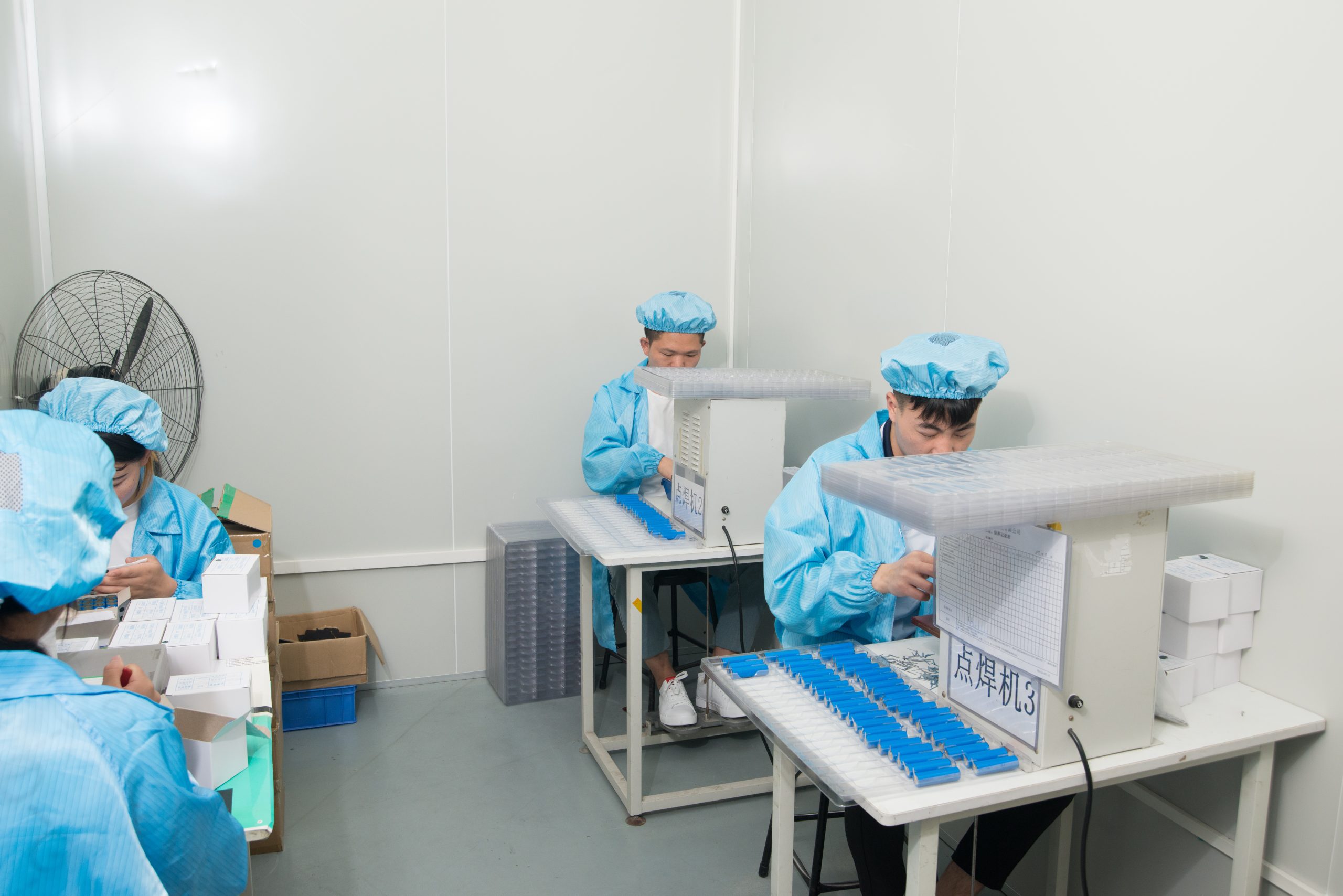

Common Electric Toothbrush Repair Methods – OEM Manufacturing Tips

Custom Logo Smart Toothbrush OEM for Austin Tech Companies
What Makes a High-Quality Water Flosser? Material Choices for Durability and Performance
.jpg)
Electric Toothbrush Shipping Solutions for OEM & Wholesale Export
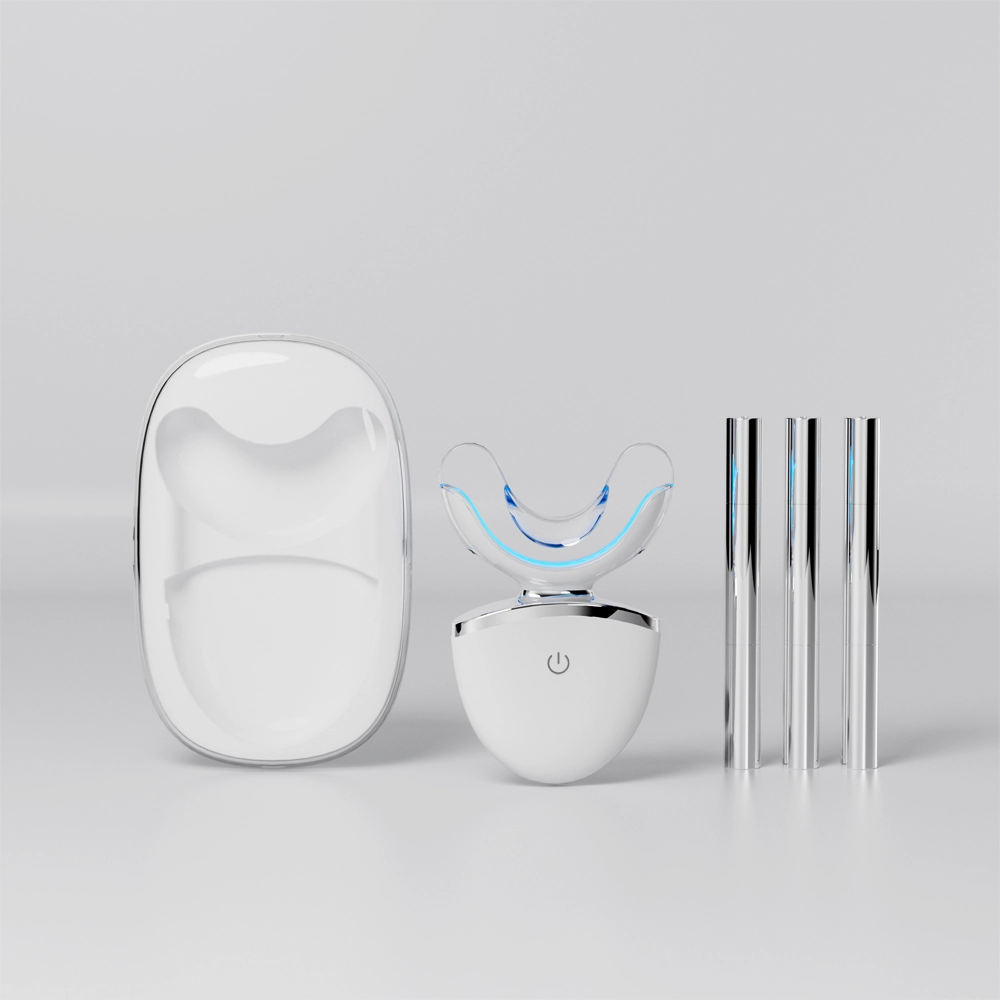

Manufacturing Trends of Smart Teeth Whitening Devices: APP Connection and Personalized Whitening Solutions