As manufacturers innovate with high-speed brush head rotation, questions arise about its impact on long-term tooth health—specifically, whether aggressive motion might accelerate enamel erosion. In this article, we’ll examine the mechanics behind rotational brushing, explore how design and user behavior interplay, and offer evidence-based guidelines to minimize enamel wear while maximizing cleaning efficacy.
First, it’s essential to understand how rotational systems work:
Thus, the combination of speed and amplitude defines the fundamental cleaning action—and its potential to stress enamel.
Moreover, enamel wear isn’t solely a function of speed:
Clinical studies show that uncontrolled high-pressure rotational brushing can accelerate enamel loss by up to 20% compared to recommended techniques.Company web:https://www.powsmart.com/product/electric-toothbrush/
Fortunately, smart engineering can mitigate these risks:
By integrating these design elements, manufacturers can deliver powerful cleaning without compromising enamel integrity.

In addition to hardware, end-user behavior plays a critical role:
Therefore, successful enamel preservation demands both well-engineered tools and proper user education.
To ensure safe performance, B2B quality teams should implement rigorous testing:
Such protocols help balance cleaning power against enamel safety in real-world use.
Finally, here are actionable recommendations to minimize enamel erosion while leveraging rotational brushing:
By combining engineered safeguards with user-centric features, manufacturers can harness the benefits of brush head rotation without elevating enamel erosion risk.
Conclusion
While high-speed brush head rotation delivers superior plaque removal, unchecked forces and improper technique can accelerate enamel erosion. By prioritizing optimized design, rigorous testing, user education, and smart integration, B2B partners can offer devices that fight plaque effectively and preserve enamel health. For collaboration on next-generation rotational-technology brushes, please contact our company!

.jpg)
Teeth-whitening-devices-safe-guide | Complete At-Home Guide

Modern technology in oral care: innovative products and services
.jpg)
Is Adaptor Compatibility Limited by Grip Ergonomics Flaws?
.jpg)
Enamel Erosion with Cavity Acceleration – Vicious Cycle?
Can People Undergoing Orthodontic Treatment Use Home Teeth Whitening Products?

Oral Irrigator Factory Tell You How to Keep Water Flosser from Spraying Everywhere
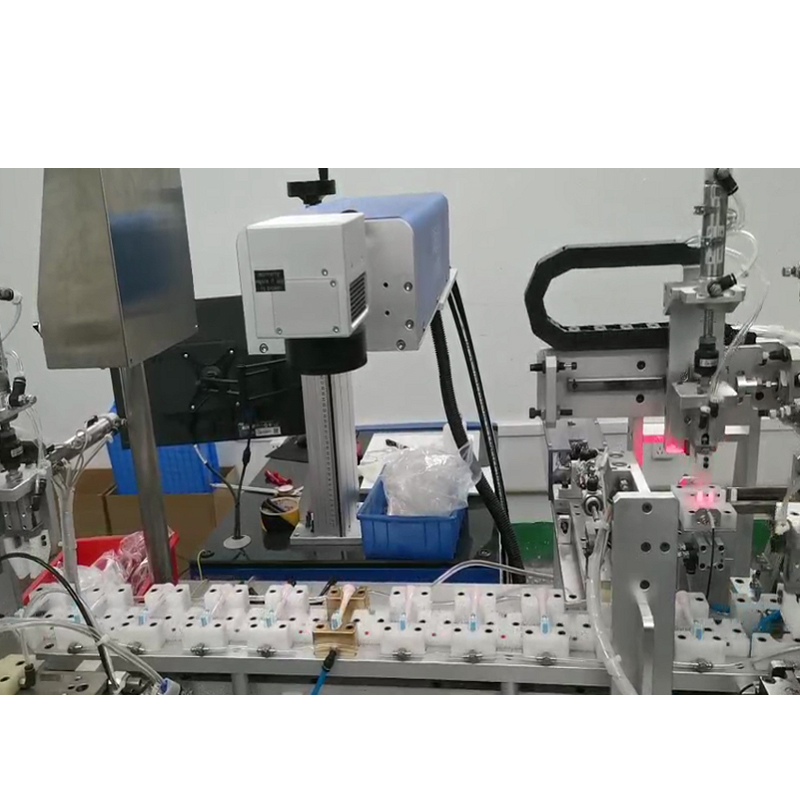
Electric Toothbrush Production Process Diagram: Complete Process from Injection Molding to Assembly and Key Points of Quality Inspection
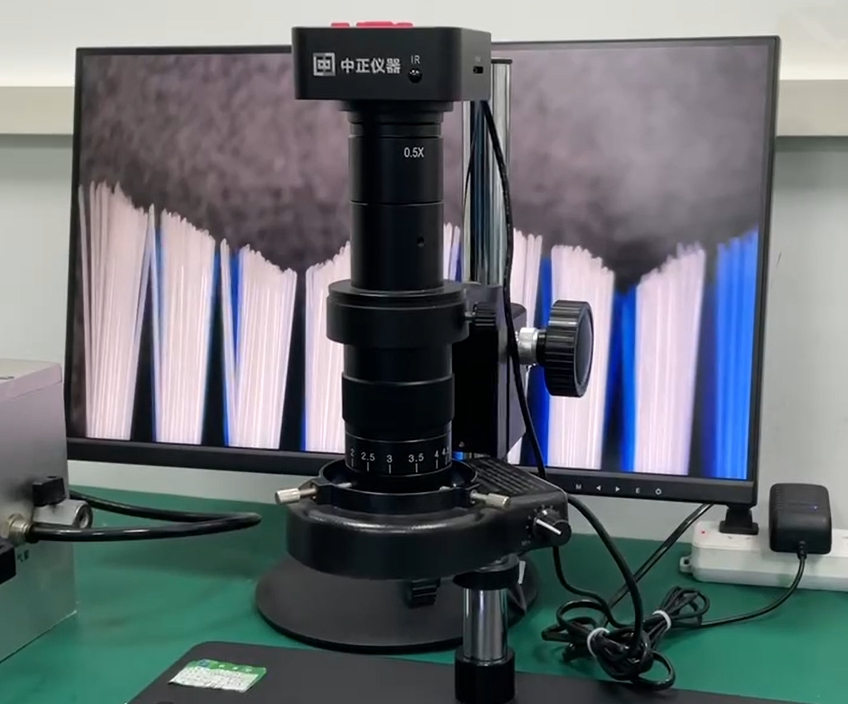

Electric Toothbrush Bristle Implantation Technology: How to Choose the Most Suitable Bristles?

Quietest Electric Toothbrush OEM Models for NYC Apartments
.jpg)
Holiday Gift Sets Smart Sonic Toothbrush Supplier WA | Corporate Gifts
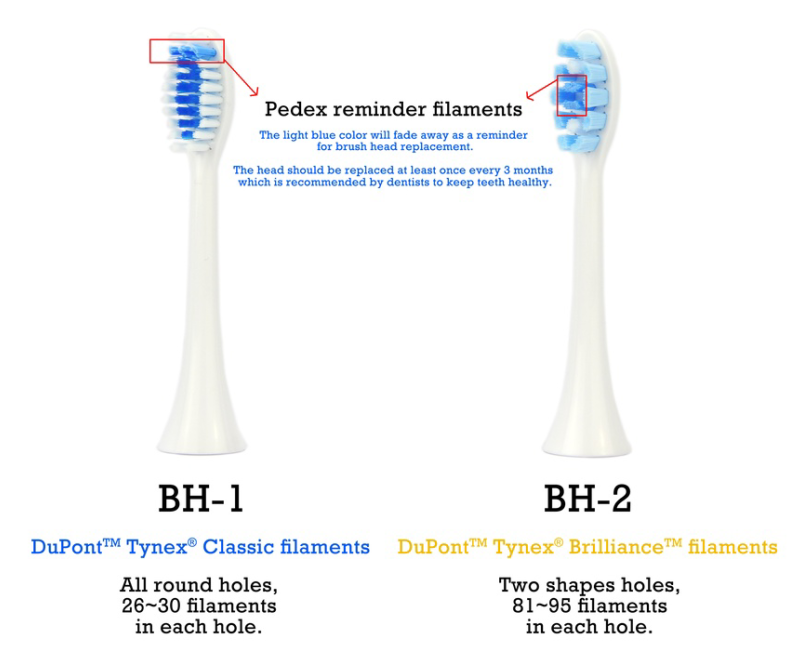
FDA-Approved Antibacterial Bristles of Electric Toothbrush: A Safety Guide for Oral Care

How a specialized Orthodontic Brush Head better cleans around braces and brackets
.jpg)
Austin Eco Toothbrush: Sustainable Oral Care from Factory to Home
.jpg)
Custom Teeth Whitening Device Factory for Global OEM Brands

Why is Quality Certification Support integral to a successful Contract Manufacturing agreement?
.jpg)
Texas Flag Pattern Toothbrush